This page presents a brief overview of digital trade within trade agreements (data comes from the 2024 TAPED dataset created by the Uni. of Lucerne)
1) Headline numbers
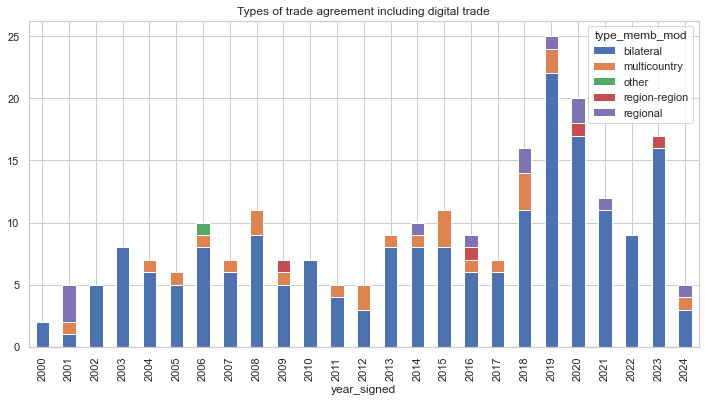
The above graph highlights the headline data -the number of trade agreements by year that include any clauses related to e-commerce or digital trade. It is divided by type of trade agreement.

In more detail, the left figure shows the % of all trade agreements in a year with clauses or whole chapters relating to digital trade/e-commerce. As shown, an increasing number of trade agreements now include this issue. Around half of agreements include a chapter on this topic.
On the right graph, we can see that for agreements with a digital trade/e-commerce chapter, the average number of articles relating to digital trade/e-commerce is increasing over time. This shows the growing depth of content
2) Rules in digital trade

The above graphs represent a more detailed analysis of the core digital trade rules as discussed on this site (i.e. here we exclude data on parallel areas such as IPR and investment related that are considered adjacent to digital trade). Doing this, in the left graph we can see that these rules are increasing on average within agreements over time, in line with the earlier graph.
The right graph shows the balance between between hard (legally binding) and soft (not legally binding) rules. Although “soft law” was an earlier trend (c. 2005-2015) within digital trade, the split between hard and soft law in digital trade rules has stayed constant at around 40% hard/60% soft within recent years.
3) Global profile
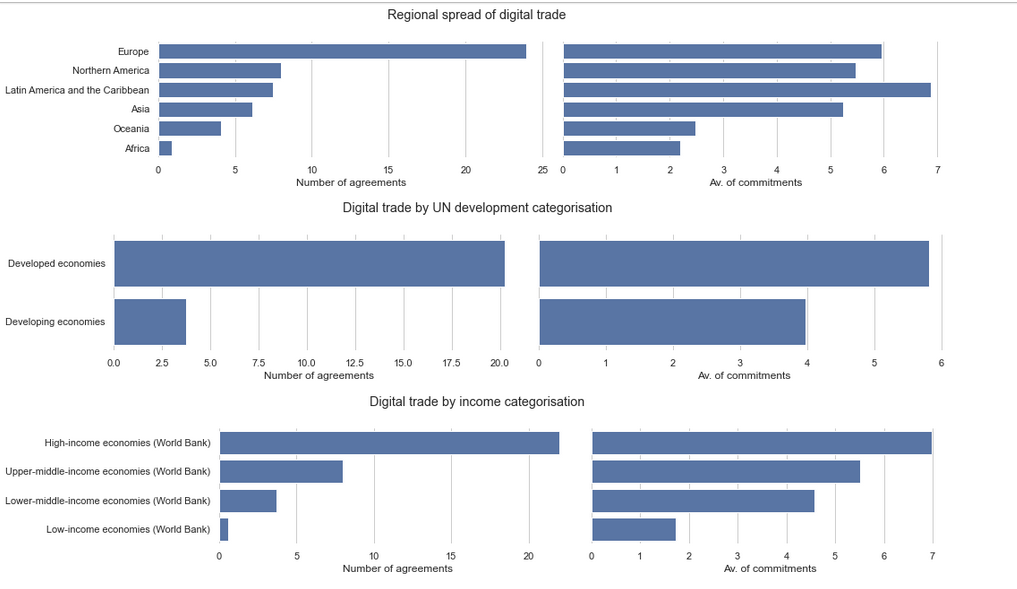
The profile below shows who is signing agreements across different country categories (in terms of number of agreements on the left and average number of commitments within each agreement).
This highlights the variation globally and that these rules are being adopted more readily by more wealth countries. (it should be noted that the EU data is skews by the large number of individual agreements that the EU signs with different countries and regions)